Table of Contents
The Long-Term Effects of Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, has become one of the most popular bariatric procedures for individuals seeking significant weight loss. This surgery involves removing a large portion of the stomach, resulting in a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach that limits food intake and helps control hunger. While the immediate benefits of weight loss are clear, it’s essential to understand the long-term effects of gastric sleeve surgery to ensure that patients are prepared for the lifestyle changes that follow.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the long-term physical, emotional, and lifestyle effects of gastric sleeve surgery. We’ll also discuss the potential complications, benefits, and what patients can expect years after the procedure. By understanding these factors, individuals can make informed decisions about whether gastric sleeve surgery is the right option for them.
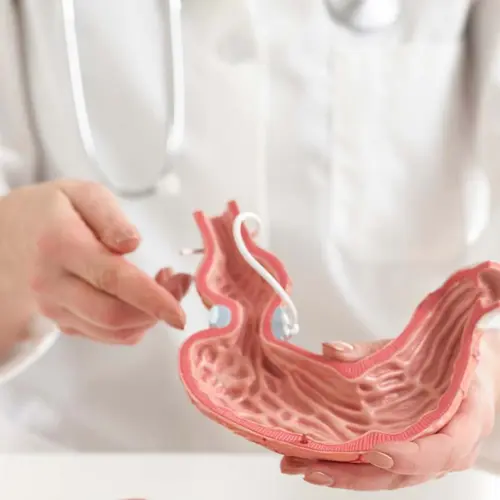
What is Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
Gastric sleeve surgery is a type of bariatric surgery that reduces the size of the stomach by approximately 75-80%. This procedure is performed laparoscopically, meaning small incisions are made in the abdomen, and the surgery is done using a camera and specialized instruments. The result is a stomach that holds much less food, leading to reduced calorie intake and significant weight loss over time.
Unlike other bariatric procedures such as gastric bypass, gastric sleeve surgery does not involve rerouting the intestines or creating a new digestive tract. This makes it a less complex procedure with fewer potential complications. However, it is still a major surgery that requires long-term lifestyle changes to maintain weight loss and overall health.
The Long-Term Physical Effects of Gastric Sleeve Surgery
1. Sustained Weight Loss
One of the most significant long-term effects of gastric sleeve surgery is sustained weight loss. Most patients lose 60-70% of their excess body weight within the first year after surgery. Over the long term, many individuals are able to maintain a significant portion of this weight loss, provided they adhere to a healthy diet and exercise regimen.
However, it’s important to note that some patients may experience weight regain several years after surgery. This can occur if individuals do not follow the recommended lifestyle changes or if the stomach stretches over time, allowing for increased food intake. To prevent weight regain, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and seek support from healthcare professionals when needed.
2. Changes in Hunger and Satiety
Gastric sleeve surgery not only reduces the size of the stomach but also affects hormones that regulate hunger and satiety. The surgery removes the portion of the stomach that produces ghrelin, a hormone responsible for stimulating appetite. As a result, many patients report feeling less hungry after surgery, which can make it easier to stick to a reduced-calorie diet.
Over the long term, these hormonal changes can help patients maintain their weight loss by reducing the frequency and intensity of hunger pangs. However, some individuals may find that their appetite gradually increases as their body adjusts to the surgery. It’s essential to remain mindful of portion sizes and avoid overeating, even if hunger levels change over time.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
Because gastric sleeve surgery reduces the amount of food that can be consumed, there is a risk of developing nutritional deficiencies in the long term. Common deficiencies include:
Vitamin B12: The reduced stomach size can impair the absorption of vitamin B12, which is essential for red blood cell production and nerve function.
Iron: Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, especially in women of childbearing age.
Calcium and Vitamin D: These nutrients are crucial for bone health, and deficiencies can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Folate: Folate is important for cell division and the production of DNA, and a deficiency can lead to anemia and other health issues.
To prevent these deficiencies, patients are typically advised to take daily vitamin and mineral supplements for the rest of their lives. Regular blood tests are also necessary to monitor nutrient levels and adjust supplementation as needed.
4. Gastrointestinal Issues
Some patients may experience long-term gastrointestinal issues after gastric sleeve surgery, including:
Acid Reflux: The smaller stomach can increase pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter, leading to acid reflux or worsening of pre-existing conditions.
Dumping Syndrome: Although more common with gastric bypass, some gastric sleeve patients may experience dumping syndrome, which occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine. Symptoms include nausea, diarrhea, and lightheadedness.
Constipation: Reduced food intake and changes in diet can lead to constipation, especially if fiber intake is low.
These issues can often be managed with dietary adjustments and medications, but it’s important to discuss any persistent symptoms with a healthcare provider.
The Long-Term Emotional and Psychological Effects
1. Improved Mental Health
For many individuals, gastric sleeve surgery leads to significant improvements in mental health and overall well-being. The weight loss that follows surgery can boost self-esteem, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and improve body image. Many patients report feeling more confident and capable of participating in activities they may have avoided due to their weight.
In addition, the physical health benefits of weight loss, such as improved mobility and reduced pain, can contribute to a better quality of life and a more positive outlook.
2. Emotional Challenges
While many patients experience improved mental health after surgery, it’s important to acknowledge that some individuals may face emotional challenges in the long term. These can include:
Body Image Issues: Even after significant weight loss, some patients may struggle with body image, particularly if they have excess skin or if they don’t lose as much weight as they had hoped.
Emotional Eating: Some individuals may turn to food for comfort during times of stress or emotional distress. After surgery, emotional eating can be more challenging to manage due to the reduced stomach size, but it can still lead to weight regain if not addressed.
Relationship Changes: Weight loss can affect personal relationships, particularly if a partner or family member is not supportive of the lifestyle changes required after surgery. Some patients may find that their relationships improve, while others may experience tension or conflict.
To address these emotional challenges, many bariatric surgery programs offer counseling or support groups to help patients navigate the psychological aspects of weight loss. Seeking professional support can be an essential part of long-term success.
The Long-Term Lifestyle Changes After Gastric Sleeve Surgery
1. Dietary Changes
One of the most significant long-term effects of gastric sleeve surgery is the need for permanent dietary changes. After surgery, patients must follow a structured eating plan to ensure they get enough nutrients while avoiding overeating. Key dietary guidelines include:
Small, Frequent Meals: Because the stomach is smaller, patients need to eat smaller portions more frequently throughout the day.
High-Protein Foods: Protein is essential for healing and maintaining muscle mass, so patients are encouraged to prioritize protein-rich foods such as lean meats, eggs, and dairy.
Avoiding Sugary and Fatty Foods: Foods high in sugar and fat can lead to dumping syndrome and weight regain, so they should be limited.
Staying Hydrated: Drinking enough water is crucial, but patients must avoid drinking fluids with meals to prevent overfilling the stomach.
These dietary changes can be challenging to maintain in the long term, but they are essential for preventing weight regain and ensuring overall health.
2. Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is a key component of long-term success after gastric sleeve surgery. Exercise helps maintain weight loss, improve cardiovascular health, and increase muscle mass. Most patients are encouraged to start with light activities, such as walking, and gradually increase the intensity and duration of their workouts as they recover from surgery.
In the long term, incorporating a mix of aerobic exercise (such as walking, swimming, or cycling) and strength training (such as weightlifting or resistance exercises) can help patients maintain their weight loss and improve their overall fitness.
3. Ongoing Medical Monitoring
After gastric sleeve surgery, patients will need to attend regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor their progress and address any potential complications. These appointments typically include:
Weight and BMI Monitoring: Tracking weight loss and body mass index (BMI) to ensure patients are on track with their goals.
Nutritional Assessments: Blood tests to check for vitamin and mineral deficiencies and adjust supplementation as needed.
Mental Health Support: Counseling or support groups to address any emotional or psychological challenges.
Ongoing medical monitoring is essential for ensuring long-term success and preventing complications.
Potential Long-Term Complications
While gastric sleeve surgery is generally safe and effective, there are potential long-term complications that patients should be aware of. These include:
Stomach Stretching: Over time, the stomach may stretch, allowing patients to eat more food and potentially leading to weight regain.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Some patients may develop or experience worsening acid reflux after surgery.
Nutritional Deficiencies: As mentioned earlier, long-term nutritional deficiencies can occur if patients do not take the necessary supplements or follow a balanced diet.
Weight Regain: While most patients experience significant weight loss after surgery, some may regain weight over time if they do not adhere to the recommended lifestyle changes.
It’s important to discuss these potential complications with a healthcare provider and take steps to minimize the risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does gastric sleeve surgery last?
Gastric sleeve surgery is considered a permanent procedure, as a large portion of the stomach is removed. However, the long-term success of the surgery depends on the patient’s ability to maintain healthy lifestyle changes, such as following a balanced diet and exercising regularly.
2. Can I regain weight after gastric sleeve surgery?
Yes, it’s possible to regain weight after gastric sleeve surgery, especially if the stomach stretches or if patients do not follow the recommended dietary and exercise guidelines. To prevent weight regain, it’s important to stay committed to a healthy lifestyle and seek support from healthcare professionals when needed.
3. Will I need to take vitamins for the rest of my life?
Yes, most patients will need to take daily vitamin and mineral supplements for the rest of their lives to prevent nutritional deficiencies. Common supplements include a multivitamin, calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor nutrient levels and adjust supplementation as needed.
4. Can I get pregnant after gastric sleeve surgery?
Yes, but it’s recommended to wait at least 12-18 months after surgery before becoming pregnant. This allows the body to stabilize and ensures that the patient is getting enough nutrients to support a healthy pregnancy. Be sure to discuss your plans for pregnancy with your surgeon before and after surgery.
5. How will my diet change after gastric sleeve surgery?
After gastric sleeve surgery, patients must follow a structured eating plan that includes small, frequent meals, high-protein foods, and limited sugary and fatty foods. Drinking enough water is essential, but patients should avoid drinking fluids with meals to prevent overfilling the stomach.
6. What are the risks of developing acid reflux after gastric sleeve surgery?
Some patients may develop or experience worsening acid reflux after gastric sleeve surgery. This occurs because the smaller stomach can increase pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter, leading to acid reflux. Medications and dietary adjustments can help manage this condition.
7. How does gastric sleeve surgery affect hunger?
Gastric sleeve surgery reduces the production of ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite, leading to decreased hunger. However, some patients may find that their appetite gradually increases over time as their body adjusts to the surgery.
8. Can I drink alcohol after gastric sleeve surgery?
It’s best to avoid alcohol for at least the first year after surgery, as it can interfere with weight loss and lead to complications. Alcohol is high in calories and can be absorbed more quickly after surgery, increasing the risk of intoxication.
9. How soon after surgery can I start exercising?
Patients can usually start light activities, such as walking, within a few days after surgery. More strenuous exercise, such as weightlifting or running, should be avoided for at least 4-6 weeks. Your surgeon will provide specific guidelines based on your recovery progress.
10. Will I have loose skin after losing weight?
It’s possible to have loose skin after significant weight loss, especially if you lose a large amount of weight quickly. Some patients choose to have cosmetic surgery to remove excess skin, but this is a personal decision and not medically necessary